GS Paper III
News Excerpt:
The growth of India's steel sector is threatened due to the European Union's restrictions on scrap metal exports.
More details on the news:
- The decision of the EU will adversely impact India as it is scrap-deficient. Imports are key to its target of doubling steel production capacity to 300 million tons by the end of the decade.
- Producers are following policy developments such as the EU’s update of its waste shipment rules, which came after China tightened scrap metal exports.
- Most countries are protecting their scrap due to a circular economy being implemented at home.
- Countries are recycling more scrap domestically to reduce the use of pollutive feedstocks like iron ore in the steel-making process.
- The EU’s proposal recommends that waste be sent only to countries outside the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) group if they can meet strict environmental criteria.

India’s dependence on the import of scrap metal:
- India is the biggest destination for European scrap after Turkey, and it buys the rest from the US, Central and South America, Asia, and the Middle East, according to the industry group.
- The country’s consumption of ferrous scrap metal will jump 50% to 60 million tons by the end of the decade, and imports will double to about 20 million tons, it estimates.
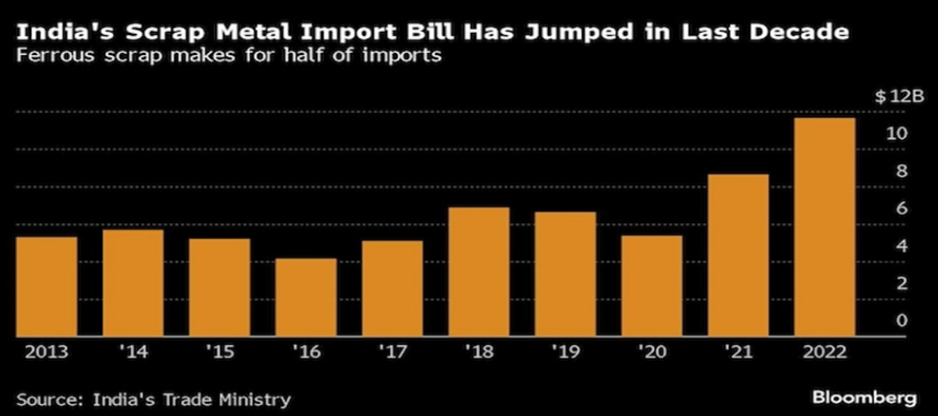
- India imported about $12 billion worth of metal scrap in 2022, more than double the amount from just five years earlier, according to trade ministry data.
- Almost half of the inflows were steel scraps, used as feedstock in electric arc and induction furnaces.
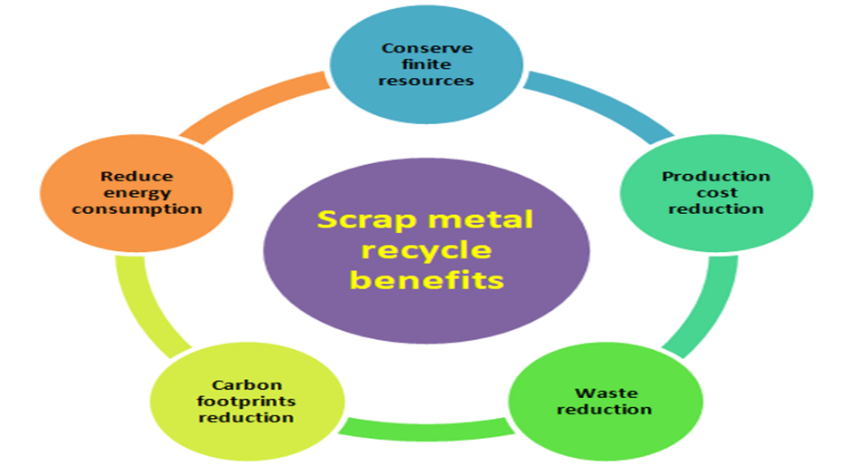
Advantages of Scrap Metal Recycle:
Challenges with scrap metal recycling in India:
- Limited recycling infrastructure: India’s recycling infrastructure is currently limited due to the low number of old vehicles being disposed of, and it will continue to rely on imports to meet its growing demand.
- Policy issue: In 2021, the government launched a scrapping policy to encourage recycling and remove old and polluting vehicles from the roads, but the uptake remains low.
- Limited investments: Advanced recycling technologies are underutilized due to limited investments. This results in a lower recycling rate and reduced product quality.
- Absence of sufficient incentives: The absence of sufficient incentives and support for recycling initiatives hampers the growth of the industry.
- Dominance of informal sector: A significant portion of scrap metal collection and recycling is carried out by informal waste pickers or small-scale collectors.
- Low quantity of disposal: Because of the low quantity of old cars being disposed of, India’s recycling infrastructure is presently restricted, and the country will continue to depend on imports to satisfy its expanding needs.

Steel scrap recycling policy of India:
- India’s steel scrap recycling policy aims to standardise the process of steel recycling in the country.
- The policy defines a working model that seeks to create a mechanism for treating waste streams and residues produced from dismantling and shredding facilities in compliance with the Hazardous & Other Wastes Rules, 2016.
- Entrepreneurs can establish collection and/or dismantling centres for the collection and sorting of scrap steel.
- The policy dictates that these facilities should be located close to a scrap processing centre.
- The objective is to produce high-quality ferrous scrap for quality steel production, thus minimizing the dependency on imports.
Way forward:
- Encourage the formalization: Encourage the formalization of this sector by providing training, safety measures, and regulatory compliance support.
- Create a stable market: To create a stable market for recycled materials, encourage the use of domestically recycled scrap metal in government infrastructure projects and procurement.
- Explore collaboration: International collaboration is required for knowledge sharing and technology transfer in the field of scrap metal recycling.
- Promote a circular economy: More circular economy initiatives are required to encourage industries to design products with recyclability in mind.
- Encourage recycling of scrap metal: Initiatives such as subsidies, tax breaks, or grants can help promote the growth of recycling infrastructure.
- Investment: Investment is required in modern collection and sorting facilities to ensure that scrap metal is efficiently gathered and sorted.
Conclusion:
Thus, achieving reduced import dependence on scrap metal necessitates sustained cooperation between the government, industry, and society. This long-term commitment is essential for building a more self-reliant and sustainable metal supply chain, benefiting the nation's economic and environmental goals.
Prelims PYQ
Q. Which of the following are some important pollutants released by steel industry in India? (UPSC 2014)
(1) Oxides of sulphur
(2) Oxides of nitrogen
(3) Carbon monoxide
(4) Carbon dioxide
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1, 3 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Mains PYQ
Q. Account for the present location of iron and steel industries away from the source of raw material, by giving examples. (UPSC 2020)
