GS Paper III
News Excerpt: According to government sources, India’s total tax receipts in 2023-24 could exceed the Budget Estimate by a “considerable margin” (a significant difference between two figures).
More on News:
- India's tax receipts for the fiscal year 2023-24 are expected to surpass the Budget Estimate.
- This optimism is driven by strong direct tax and GST collections, which are anticipated to continue their momentum.
- The final picture will become clearer with data on advance tax payments in the third quarter and GST collections for April-December.
- On the GST front, authorities foresee 13-14% year-on-year growth in collection, with monthly averages reaching Rs 1.7-1.8 trillion in 2024-25.
- Various policy measures and action plans by the revenue department have contributed to this success.
- With a collection of Rs 1.72 trillion in October, the highest ever in a month after the Rs 1.87 trillion reported in April, the monthly average GST mop-up this financial year stands between Rs 1.6 trillion and Rs 1.65 trillion.
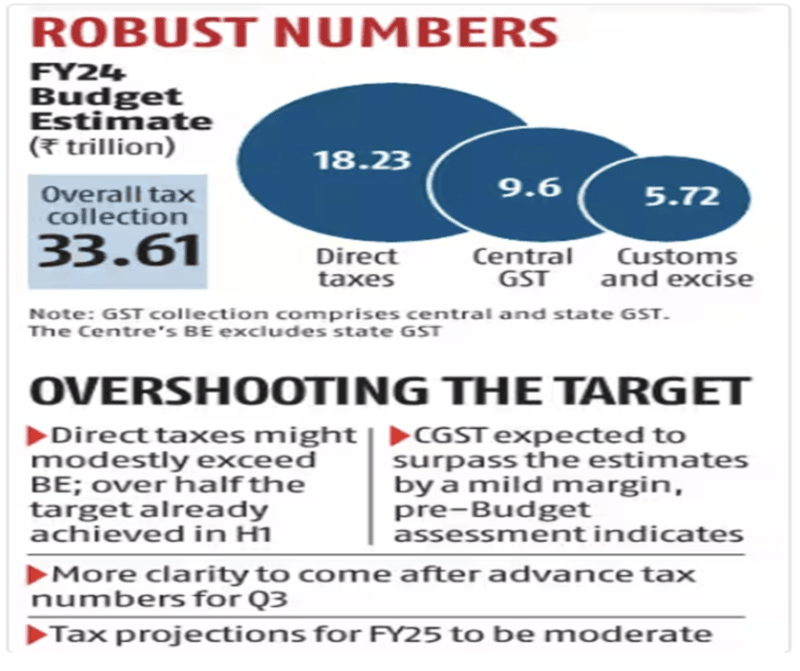
- Taking both direct and indirect taxes, the gross collection is expected to grow 10.45 % to Rs 33.61 trillion in 2023-24.
- The government has projected 10.5 % growth in revenues from corporate and individual income tax to Rs 18.23 trillion in the current financial year. And, GST collection is projected to grow 12 % to Rs 9.56 trillion.
- On the direct tax front, gross collection is expected to grow 10.1 % year-on-year, and net collection 11.1 %, in 2023-24.
- Corporation and personal income-tax revenues are estimated to grow 11.7% and 11.4 percent, respectively.
Revenue receipt: Revenue receipts consist of tax revenues, non-tax revenues, State’s share of Union taxes and duties and grants-in-aid from Government of India.
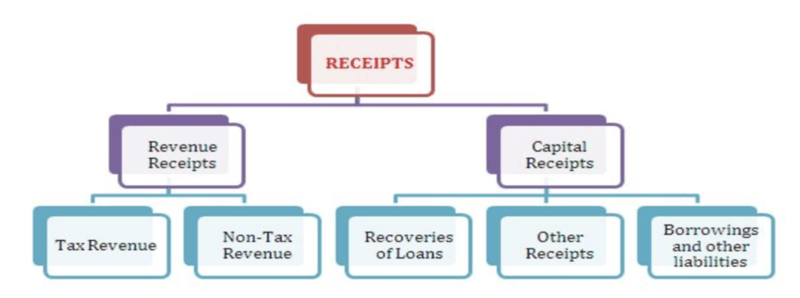
Tax Revenue:
- Tax Revenue forms part of the Receipt Budget, which in turn is a part of the Annual Financial Statement of the Union Budget.
- It gives a detailed report on revenue collected from different items like corporation tax, income tax, wealth tax, customs, union excise, service, taxes on Union Territories like land revenue, stamp registration etc.
- Taxes collected from both direct and indirect tax are considered in Tax Revenue.
Non-Tax revenue
- Non-Tax Revenue is the recurring income earned by the government from sources other than taxes.
- The most important receipts under this head are interest receipts (received on loans given by the government to states, railways, and others) and dividends and profits received from public sector companies.
- Various services provided by the government - police and defence, social and community services such as medical services, and economic services such as power and railways also yield revenue for the government.
- Though the Railways are a separate department, all their receipts and expenditures are routed through the Consolidated Fund.

Capital receipts:
- Capital receipts comprise miscellaneous capital receipts such as proceeds from disinvestment, recoveries of loans and advances, debt receipts from internal sources (market loans, borrowings from financial institutions/commercial banks) and loans and advances from Government of India as well as accruals from the Public Account.
Prospect of tax collection and economic growth:
- India's economy is expected to grow by over 6%.
- Factors contributing to this growth include the formalization of the economy, data integration, and improved compliance.
- Tax buoyancy (higher tax collections compared to economic growth) is expected to remain robust.
- This increased tax revenue should provide some cushioning to government spending, which might be impacted by the likely extension in the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana.
- Excise duty collections might be challenging due to current trends, particularly for petroleum and tobacco, while achieving Customs targets is expected to be less difficult.
Conclusion: India's optimistic outlook on tax receipts for the fiscal year 2023-24, driven by strong direct tax and GST collections, reflects positive economic growth trends and improved compliance. This surplus revenue may provide crucial support to government spending in the face of potential challenges, such as the extension of welfare programs and fluctuations in excise duty collections.
Prelims PYQ
Q. Consider the following statements: (UPSC 2017)
- Tax revenue as a percent of GDP of India has steadily increased in the last decade.
- Fiscal deficit as a percent of GDP of India has steadily increased in the last decade.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
