Mizoram has the highest rate of cancer in India
Relevance: GS III (Science and Technology – Diseases and Biotechnology)
Why in News?
Despite being the country’s second least populated state, Mizoram exhibits the highest cancer incidence rate in India.
About Cancer:
Cancer is a disease in which some of the body's cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body. Cancer can start almost anywhere in the human body, which is made up of trillions of cells.
Lancet Report on Cancer for South Asia (Regional wise):
- Lung, prostate, colorectal, stomach and liver cancer are the most common types of cancer in men, while breast, colorectal, lung, cervical and thyroid cancer are the most common among women.
- Recently, among new cases, breast, cervix, and lung cancer were the most frequently reported in South Asian region and India too.
- The causes stated according to Lancet reports were - economic transitions, lifestyle changes (such as physical inactivity), and rising obesity prevalence are increasing cancer risk in this region, with existing risk factors such as tobacco use and indoor and outdoor air pollution.
Indian Scenario:
- Cervical cancer is the second most common cancer among women in India. Experts estimate that 90,000 women develop cervical cancer in India annually.
- The standard treatment for Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer (LACC) involves a medicine called cisplatin given alongside radiotherapy — the concurrent treatment also called The five-year disease-free survival rate was 73% in women who received the induction therapy before chemoradiation, compared with 64% in women who received only chemoradiation.
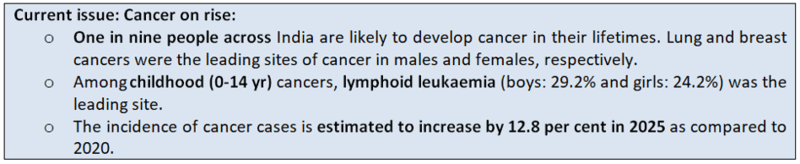
- Mizoram has the highest rate: Cancer incidence and mortality are also growing among the younger generation in Mizoram, which may stem from static lifestyle and dietary patterns prevalent with the endogamous tribal population, potentially contributing to a genetic predisposition.
- Observations in Mizoram:
- Meanwhile, findings in Mizoram note that among men the most prevalent cancer site was the stomach, followed by head and neck, lung, oesophagus, colorectal, liver, urinary, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and prostate cancers.
- Conversely, among women, lung cancer exhibited the highest incidence followed by cervical, breast, stomach, head and neck, colorectal, oesophagus, liver and ovarian cancers.
- Locally advanced cervical cancer (LACC) has a major impact on the lives of Indian women with an estimated 122,844 new cases of cervical cancer in the year 2012. About 80% of these cases present in a locally advanced stage leading to high morbidity and mortality.
Way Forward:
- Prevention and Early Detection: Although cancer is a life-threatening disease, it can be prevented and treated if detected early. Screening programs such as breast self-examination and mammography substantially increase breast cancer survival.
- Need for proper database and registries: Official cancer registries don’t reflect reality due to a lack of funding and low awareness. Awaking the public about deadly diseases like Cancer is necessary at the local governance level because many cases of brain and breast cancer especially in rural women go unregistered in India.
- Better screening and treatment centres are needed: Many women in India face barriers to accessing healthcare. Their headaches, stemming from a developing brain cancer, are ignored generally in many cases. More comprehensive linkages between screening centres and hospitals are essential to reduce cancer mortality in the country.
- In order to reduce mortality, it is important to ensure that people get diagnosed early on and receive timely treatment.
- There must be more investment in infrastructure and many more cancer care facilities.
- Low-cost drugs can improve survival: According to the global clinical trial, a short weekly chemotherapy course with two inexpensive medicines given ahead of standard chemoradiation treatment can significantly improve survival in locally advanced cervical cancer. In short, a ‘new standard of care is required’.
- Improvement in Policy and programme implementation: There are several programmes of the government that are working independently and in silos. They need to be coordinated so that once a person is screened, they do reach a hospital.

United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) data dashboard
Relevance: GS III (Environment; Climate change and Land degradation)
Context
The UNCCD Data Dashboard released national reporting data from 126 nations and demonstrates how rapidly land degradation is progressing in all areas.

About
- Land degradation is the deterioration or loss of the productive capacity of the soils for the present and future.
- Land desertification is used to describe land deterioration in dryland regions, which include arid, semi-arid, and dry sub-humid zones. The process of drylands losing biological productivity as a result of natural or artificial influences is known as desertification. It doesn't imply that already-existing deserts will get bigger.
- Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN) refers to a condition in which the quantity and quality of land resources required to sustain ecosystem functions and services and improve food security either stay constant or grow. For 2030, 109 nations have voluntarily established LDN objectives.
According to the UNCCD data dashboard:
- By the end of 2019, 9.5% of the nation's land area, remained in a degraded state. In 2015, this percentage was only 4.4% of India's total land area.
- 36.8% of India’s land area is drought-prone and 83.85% of the Indian population is exposed to drought situations.
- 18.39% of India's population, were vulnerable to land degradation.
- 50.49% of the global land area is drought-prone while the Eastern and Central Asia, Latin America and Caribbean regions experience the most severe degradation.
Land degradation and desertification:
Causes:
- Deforestation, causes of which go beyond tree felling, which increases the risk of fires, among others.
- Poor agricultural practices, from not rotating crops to unprotected soils or chemical fertiliser and pesticide use, etc.
- Overexploitation of natural resources as a consequence, for example, of irresponsible management of vegetation or water.
- Bad livestock practices, such as overgrazing, which severely erode the land and prevent the regeneration of vegetation
Threats to land integrity:
- Increasing and combined pressures of agricultural and livestock production (over-cultivation, overgrazing, and forest conversion)
- Urbanization and Deforestation
- Extreme weather events like droughts and coastal surges, increase the salinity in the land.
Impacts:
- Pressure on Non-renewable sources: The world's arable lands and pastures, which are necessary for the provision of clean air food water, are under stress.
- Impact on Food-web and life cycle: It negatively affects food production, livelihoods, and the development and provision of other ecosystem goods and services.
- Increase in Migration and Refugee issue: Populations are under pressure to relocate to more favourable locations as a result of water supplies drying up, degrading soil, and the expansion of deserts in certain areas.
- Impact on health and Sanitation: Due to decreased food and water supplies, decreased hygiene and a lack of clean water, respiratory illnesses brought on by air pollution and dust from wind erosion, and the spread of infectious diseases as a result of population migration.
Measures undertaken by India:
- One of the eight missions under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) –
- The National Mission for a Green India (GIM) seeks to maintain, restore, and enhance India's forest cover while also adapting to climate change. Ten million hectares of forest and non-forest land are the goal under the mission to enhance the amount of forest cover and the quality of the current forest, therefore assisting in reducing land degradation.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS), Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP), Drought Prone Area Programme (DPAP), National Rural Drinking Water Programme (NRDWP), Swarna-Jayanthi Grameen Swarozgar Yojana (SGSY), Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY), Fodder & Feed Development Scheme etc.
- India is committed to restoring 26 million hectares of degraded and deforested land by 2030 as part of the Bonn Challenge.
- Also, the Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas of India is published by ISRO.
Way forward:
- Achieving Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN) principles given by UN Convention to combat desertification, requires three actions:
- Firstly, avoiding new degradation of land by maintaining existing healthy land.
- Secondly, reducing existing degradation by adopting sustainable land management practices that can slow degradation while increasing biodiversity, soil health, and food production.
- Thirdly, ramping up efforts to restore and return degraded lands to a natural or more productive state.
- The government should look for medium and long-term drought mitigation requirements, sustainable ecosystem service delivery, opportunities for cooperation with other social, economic, and environmental goals, and the reinforcement and promotion of inclusive and responsible land governance.

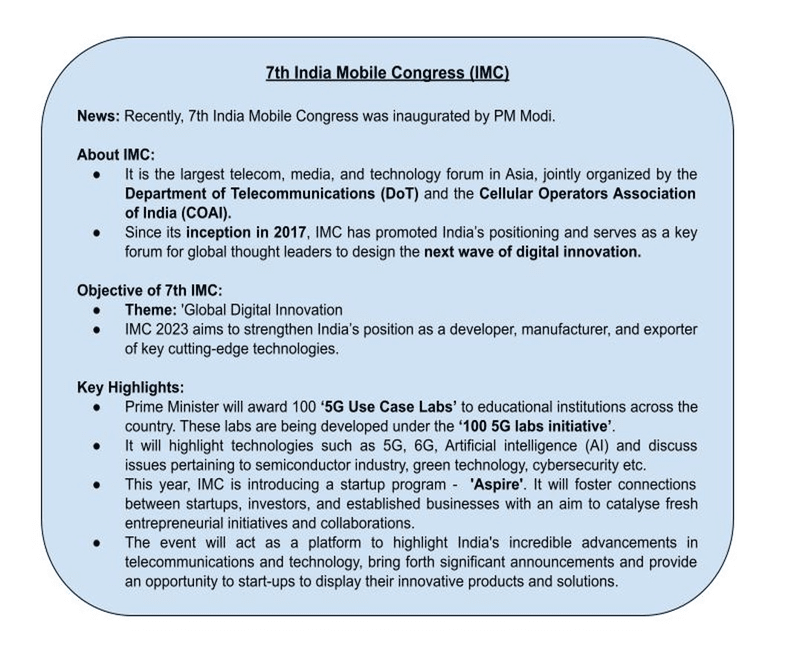
India Aims to Lead In ‘6G'
Context
Prime Minister of India announced India's ambitious advancements in 6G technology while inaugurating the 7th India Mobile Congress (IMC).
Evolution of Cellular Networks:
- First Generation:
- It operated at 2.4 kbps with a 30 KHz channel capacity.
- It had little security against hackers, suffered from dependability issues and signal interference, and could only be used for voice conversations.
- Second Generation:
- 2G networks offered bandwidths ranging from 30 KHz to 200 KHz and enabled users to transmit SMS and MMS messages at up to 64 Kbps, albeit at slow speeds.
- Third Generation:
- 3G technology authorized data speeds of up to 14 Mbps.
- It allowed users to make video calls, surf the web, share files, play online games, and even watch TV online.
- Fourth Generation:
- The advent of 4G signalled the beginning of the era of smartphones and portable electronic devices.
- It is the first generation to use Long-Term Evolution (LTE) technology to have potential download rates between 10 Mbps and 1 Gbps.
- It helped deliver improved latency (less buffering) for end users, and enhanced voice quality, instant messaging and social network services, and streaming quality.
- Fifth Generation:
- 5G makes possible a brand-new type of network intended to link almost everyone and everything, including devices, machines, and things.
- More consumers will be able to enjoy more consistent user experiences, huge network capacity, ultra-low latency, and higher multi-Gbps peak data rates.
About 6G:
- 6G will emerge as the sixth generation of wireless communications succeeding the 5G wireless technology, which is still untapped in many countries.
- 6G uses tremendously high frequency (THF) waves, also known as sub-millimetre waves, to achieve speeds 100 times faster than 5G - which, in comparison, uses millimetre waves (mmWave).
- Enabling 6G, the latency is expected to be less than one microsecond with increased bandwidth to accommodate enhanced connectivity.
Potential horizons of 6G:
- Immersive Extended Reality (XR):
- Extended Reality (XR) includes Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR).
- 5G is unable to support XR because of existing hardware constraints and a lack of wireless capabilities. 6G will bridge the gaps in this situation.
- Mobile Holograms:
- The advancements in high-resolution rendering, wearable displays, and ultra-speed wireless networks will enable mobile devices to display holograms.
- Holographic display requires a high rate of data transfer, that 6G provides.
- Digital Replica:
- A virtual clone of a real physical object serving as a real-time digital twin is called a digital replica.
- Users will be able to watch, track, and investigate real entities in a virtual world free from temporal and spatial limitations.
- Through the integration of robotics and Digital replication, users can physically move a robot in the real world by virtually controlling its digital twin.
Challenges for 6G to Overcome:
- Path-loss:
- The biggest challenge for 6G is to counteract the atmospheric absorption and severe path-loss of the terahertz waves. The current 5G networks face this issue too.
- Hardware challenge:
- It requires tremendous improvements in the hardware and computing capabilities of mobile phones.
6G and Sustainability:
- As per the World Economic Forum report, digital technologies including 5Gthe have the potential to reduce worldwide emissions by 15%.
- With increased efficiency and sustainability standards, 6G aims higher.
- 6G is anticipated to be crucial to accomplishing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) set forth by the UN.
- Global living standards will rise as a result of 6G's hyperconnectivity and information accessibility.
Conclusion:
Although it has a large list of obstacles to overcome, the advantages it provides are too revolutionary to ignore. Existing emergent technologies like cloud gaming, cloud storage, VR, and AR will take on a whole new dimension with the arrival of 6G. More significantly, it will contribute to the development of novel technologies like digital duplication, holographic displays, and XR - an essential step towards the future of wireless technology.
Additional information:

Also in News
Avian flu in Antarctica
Context
Recently, the first case of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) was detected in Skua (a predatory seabird) in the Antarctic region.
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI):
- Scientists have detected the presence of avian flu for the first time in the Antarctic region, raising concerns for remote populations of penguins and seals.
- HPAI viruses cause severe disease and high mortality in infected poultry.
- Only some avian influenza A (H5) and A (H7) viruses are classified as HPAI A viruses, while most A (H5) and A (H7) viruses circulating among birds are LPAI A
- The virus is known to spread among birds and mammals due to predators and scavengers feeding on infected birds. In recent cases, marine mammals have also been found to be infected.
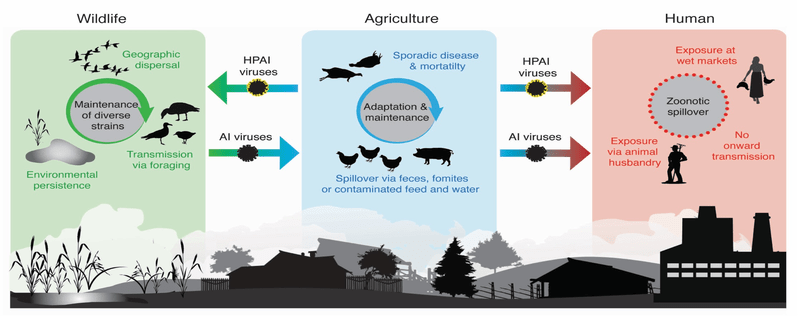
Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza (LPAI):
- Low pathogenic avian influenza viruses cause either no signs of disease or mild disease in chickens/poultry (such as ruffled feathers and a drop in egg production).
- Most avian influenza A viruses are low pathogenic and cause few signs of disease in infected wild birds.
- In poultry, some low-pathogenic viruses can mutate into highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses.
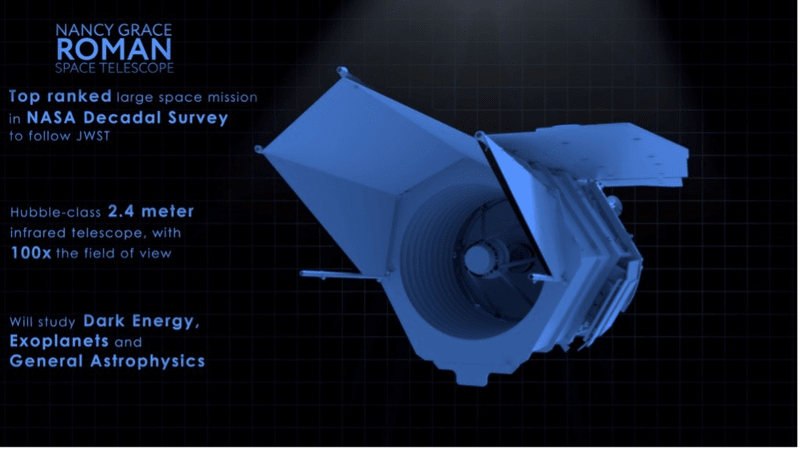
Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
Context
NASA is gearing up for humanity's deepest-ever peek into the heart of our Milky Way Galaxy.
About:
- The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (shortened as Roman or the Roman Space Telescope, and formerly the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Telescope or WFIRST) is a NASA infrared space telescope in development and scheduled to launch by May 2027.
- Roman will provide a panoramic field of view that is 200 times greater than Hubble's infrared view.
- Using a wide field instrument, Roman will survey billions of galaxies, and black holes, and catch the light of stellar explosions in a quest to solve the mystery of dark energy, which is causing the universe’s expansion to speed up.
- Roman’s scans of the sky will uncover thousands of exoplanets beyond our solar system, including types of planets never surveyed before.
Earth-like tectonic plates on ancient Venus
Context
A report published in the journal ‘Nature Astronomy’ noted that Venus may have experienced tectonic activity about 4.5 billion to 3.5 billion years ago.
Findings of the report:
- Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that describes how Earth’s thin outer shell is broken into big pieces called tectonic plates, which float on the planet’s
- Plate tectonics gave rise to oceans, continents and mountains, along with playing a critical role in nourishing life on Earth.
- New research suggests Earth’s sister (Venus) may have been home to microbial life billions of years ago due to tectonic activities.
- The plate tectonics would have likely ended on Venus after it lost water and its atmosphere got too hot and thick. This process may have dried up the necessary ingredients that make tectonic movements possible.
Reference fuels
Context
Recently, India began producing 'reference' petrol and diesel.
About:
- Reference fuels (Gasoline and Diesel) are premium high-value products, used for calibration and testing of vehicles by Auto Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEM).
- Automobile manufacturers and testing agencies like ICAT (International Centre for Automotive Technology) and ARAI (Automotive Research Association of India) use these fuels for the calibration and testing of vehicles.
- Currently, these reference fuels are being imported by India from select companies in Europe and the
- Indian Oil has established facilities for the production of gasoline reference fuels, with available grades of E0, E5, E10, E20 and E85, at its Paradip refinery and diesel reference fuel (B7 grade) at Panipat refinery.
FLAMINGO project
Context
FLAMINGO simulation leaves scientists stumped over S8 tension.
About:
- It is a project of the Virgo consortium for cosmological supercomputer simulations.
- The project has conducted a computer simulation that incorporates both dark matter and ordinary matter to study the distribution of matter in the universe.
- However, the simulation did not provide a solution to the S8 tension, which refers to contradictory results obtained from cosmological
- The project's findings suggest that there may be shortcomings in our understanding of the standard model of cosmology or physics, and that dark matter may have exotic properties
Rashtriya Gokul Mission
Context
There is a threat to other indigenous breeds as the Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) has ended up promoting only the Gir cow variety.
About the mission:
- The RGM has been implemented for the development and conservation of indigenous bovine breeds since December 2014.
- The scheme is important in enhancing milk production and productivity of bovines to meet the growing demand for milk.
- The scheme is also continued under the umbrella scheme Rashtriya Pashudhan Vikas Yojna (2021-2026).
- The RGM will result in enhanced productivity and the benefit of the programme will percolate to all cattle and buffaloes of India, especially with small and marginal farmers.
Gir cow:
- The Gir cow, a famous Indian-born dairy cattle breed is native to the Gir hills and forests of
- Other names include Bhodah, Desan, Gujarati, Kathiawari, Sorthi and Surti.
- These cattle, which were exported to Brazil in the early twentieth century have now led to the development of separate dairy (Gir Leiteiro) and beef strains.
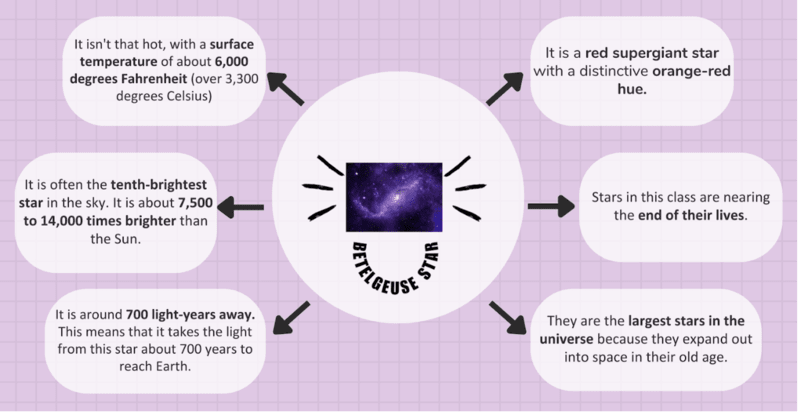
Supergiant Betelgeuse star
Context:
Recently, scientists have established why the red supergiant star Betelgeuse turned dim between 2018 and 2020, dismissing theories that suggested that the star might be entering the last stage of its evolution - Supernova or the ultimate explosion.
Cause of the dimming:
- Scientists observed that when the star appeared dim, its photosphere was brightened up.
- As per them, the dimming was due to a burst of dust, in the form of silicon monoxide, coming from the star.
- The burst might have been caused by a sudden cooling of the star's surface.
- The changes in the structure of the photosphere and the silicon monoxide are consistent with both the formation of a cold spot on the star’s surface and the ejection of a cloud of dust.
Betelgeuse star: