Need for climate-smart agriculture in India
"Sustainability is about meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs." - Gro Harlem Brundtland
Relevance: GS III (Agronomy and Environment)
- Prelims: Government Initiatives; Global Hunger Index;
- Mains: Inclusive Growth; Major Crops and issues associated with it; Sustainable Farming; Sustainable Development Goal;
Why in the News?
In India, crop yield declined owing to climate change (between 2010 and 2039) was up to 9%.

The two major issues in the 21st century faced by Humanity are:
1) Climate Change:
- Some of the ongoing effects of climate change are heat waves, flash floods, droughts, and cyclones, negatively influencing lives and livelihoods.
- The world’s southern continents are reportedly experiencing severe drought due to climate change, which negatively impacts agricultural production and farmers’ livelihoods.
2) Food Insecurity:
- Up to a certain point, rising temperatures and CO2 can benefit crops. But rising temperatures also accelerate Evapotranspiration from plants and soils, and crops must have enough water to thrive.
- For water-constrained areas, climate change will increasingly cause adverse impacts on agricultural production through diminishing water supplies, increases in extreme events like floods and severe storms, heat stress, and increased prevalence of pests and diseases.
- Both population expansion and dietary changes are contributing to an increase in the demand for food. The effects of the environment on farm output only add to the difficulty.
- As a result of climate change, traditional farming practices are becoming less productive.
How can agricultural output be increased while maintaining ecological stability? (Way Forward)
The future impacts of climate change on agricultural productivity could be substantial.
1) Climate-smart agriculture (CSA): Climate-smart agriculture is an approach for transforming food and agriculture systems to support sustainable development and safeguard food security under climate change.
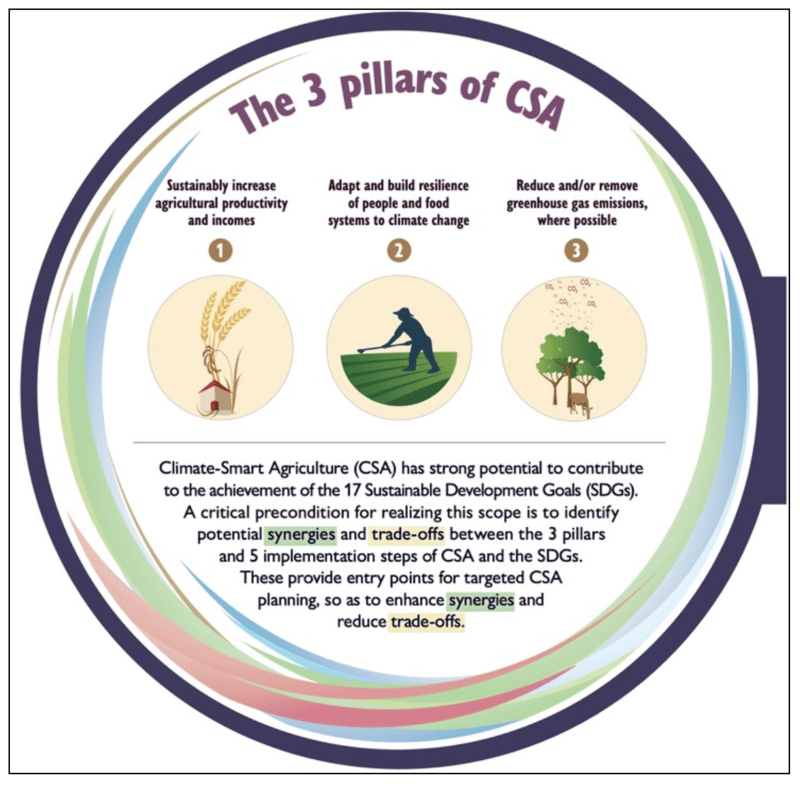
It’s Significance as a unique juncture:
- Can sustain Climate-change impacts: Dimensions of climate-smart practices include water-smart, weather-smart, energy-smart, and carbon-smart practices. They improve productivity, deal with land degradation, and improve soil health.
- Ability to combat food insecurity: It can improve food security, empower farmers, and protect our delicate ecosystems by merging innovation, resilience, and sustainability.
Hence, CSA stands out as a source of inspiration and transformation for a world working to ensure a sustainable future.
2) Community-supported efforts:
- Promoting crop diversification increases water efficiency and integrates drought-resistant crop types, all of which will help lessen the disruptive effects of climate change. Furthermore, it aids in enhancing farmland carbon storage.
- This collaborative effort helps to safeguard native plant species, keep pollinator populations stable, and mitigate the effects of habitat degradation.
- This correlation is a desired consequence and essential for long-term food security and sustainable resource usage in a warming planet.
A radical reform of the agriculture industry is required as follows:
- Precision farming: Using climate data, farmers can make site-specific and data-driven decisions to enhance efficiency, minimise resource wastage, and reduce environmental impacts.
- Site-specific No-tillage Method: The study from the northwest Indo-Gangetic Plain for wheat production shows that site-specific no-tillage is advantageous for fertiliser management and can boost yield, nutrient usage efficiency, and profitability while lowering GHG emissions.
- National Action Plan on Climate Change: It emphasises the role of climate-resilient agriculture in India’s adaptation measures. Programs such as the Soil Health Card Scheme use precision nutrient management to optimise agricultural methods.
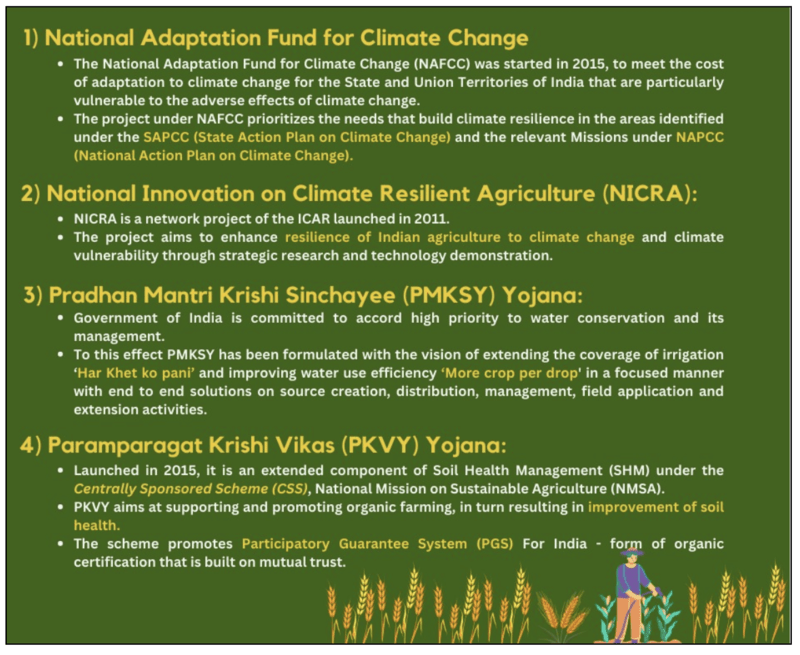
- The National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change, National Innovation on Climate Resilient Agriculture, Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana, Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana, Biotech-KISAN, and Climate Smart Village are also a few initiatives that can help.
- Sustainable Development Goal 2: The United Nations aims to end hunger and enhance environmental management; CSA’s foundation is in achieving these goals through sustainable agriculture and rural development.
- Public-Private Partnership: Various public and private sector entities, such as farmer-producer organisations and NGOs, can work towards adopting CSA.
BEYOND EDITORIAL:
Some Government Initiatives to combat Climate Change effect on Agronomy:
Mains PYQ
Q. What are the major reasons for declining rice and wheat yield in the cropping system? How crop diversification is helpful to stabilize the yield of the crops in the system? (UPSC 2017)
Q. 'Climate change' is a global problem. How India will be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (UPSC 2017)
Prelims PYQs
Q. With reference to the ‘Global Climate Change Alliance’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is an initiative of the European Union.
- It provides technical and financial support to targeted developing countries to integrate climate change into their development policies and budgets.
- It is coordinated by the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD).
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3


