A revival of the IMEC idea amid choppy geopolitics
Relevance: GS II (International Relations)
- Prelims: India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC); Abraham Accords
- Mains: Recent Geopolitical and Economical challenges;
Why in the News?
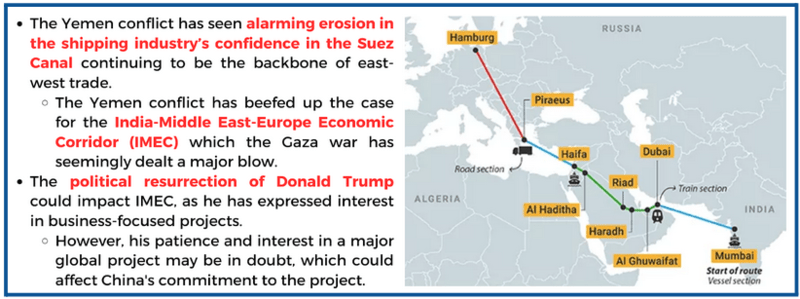
What are the challenges faced by IMEC?
The IMEC faces several challenges, including:
- Geopolitical challenges: The corridor spans diverse nations with complex geopolitics, and navigating these tensions will be crucial for the project's success. Shippers are not balking at taking the long, circuitous voyage around Africa.
- Economic challenges: Some economists and regional experts have expressed reservations about the feasibility of achieving IMEC's objectives, such as cutting transportation costs and boosting trade.
- Critics of IMEC say the Arab Street would simply not allow any major trade link between Saudi Arabia and Israel many years after the Gaza war ends.
- Regulatory challenges: The project's implementation will require coordination and cooperation among multiple countries, which may face regulatory hurdles and bureaucratic delays.
- Rail projects such as Etihad Rail and the GCC Railway (Gulf Railway), one of whose routes is proposed to terminate at Al Haditha, are already underway in the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia independently, which would dovetail with IMEC that targets ports such as Fujairah (UAE) and Jebel Ali (UAE).
- Security challenges: The IMEC is likely to face significant security challenges, including threats from extremist groups and illicit activities due to geopolitical rivalries.
- Interstate tensions: Conflicting interests of trade powers may result in power struggles and potential resistance during the project's implementation.
- A United States government press release of September 9 on the IMEC memorandum of understanding promised that stakeholders would meet within 60 days to flesh out the details, but the Gaza war has ensured that no such meeting could possibly happen.
- Uncertainty: The Israel-Hamas war has added further complexity to the initiative, and its outcome remains uncertain at the time of writing.
There will be a changed West Asia:
- Post Gaza war: Geopolitics is probably the biggest hurdle before IMEC. According to the Studies at the Observer Research Foundation, after the Gaza war, West Asia will look much different.
- Turkey, which has been explicitly left out of IMEC, has already been expressive about its irritation and proposed an alternative to Saudi Arabia and Israel through Iraq and itself to access the Mediterranean.
- Turkey will eventually be brought into the project. He is also optimistic that the long-term trend towards greater trade and strategic links between Israel and Arab nations that was championed by the Abraham Accords will hold.
- The political resurrection of Donald Trump has two implications:
- IMEC will be the sort of project that would sync with a business-focused Trump if he were to become President of the U.S. again.
- His patience and interest in a major global project, bolstering China’s doubts regarding U.S. commitment towards the IMEC. Chinese experts doubt the infrastructural proposals that IMEC is promising, critiquing the US's pattern of making empty promises.
|
The Abraham Accords The Abraham Accords are a series of bilateral agreements on Arab-Israeli normalization, signed between Israel and the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain on September 15, 2020. Key aspects of the Abraham Accords include:
The Abraham Accords have the potential to transform commerce on the Arabian Peninsula and deepen physical connectivity between the participating countries, unlocking commercial opportunities and reshaping global trading routes. |
What are the specific goods that will be transported through IMEC?
- IMEC being a multi-modal corridor offers shippers a choice of transportation modes, giving them the flexibility to choose the most cost-effective mode of transportation.
- The specific goods that will be transported through the IMEC include a wide range of products, such as apparel items, smart-phones, and high-value chips and semiconductors.
- Besides trade, electricity and digital cables, IMEC is proposed to carry hydrogen pipelines.
1) Hydrogen:
- The corridor will also facilitate the transportation of clean energy, such as hydrogen, and support the development and export of clean energy technologies.
- As the world moves towards decarbonization, hydrogen produced from fossil fuel-based processes such as methane reforming will continue to be the transition fuel until electrolysis or other “green” processes become practical.
- Hydrogen sourced from fossil fuels would keep Gulf nations in business in the hydrogen economy too with the corridor serving that purpose.
- However, as it has been proposed, IMEC is not designed to transport crude and fuel, which are Europe's main imports from the Gulf.
2) Indian Scenario and Containerization:
- Containerization through rail and road is a significant aspect of IMEC for India, as it seeks to lower logistics costs to global levels by 2030.
- India’s National Logistics Policy, unveiled in 2022, seeks to lower logistics costs to global levels by 2030. Beefing up containerization would be a key pathway towards achieving that goal.
- In India, some 70% of containers move by road but optimum splits should be 30% road, 30% rail and the rest, coastal and inland shipping. Road is faster but rail movement of containers is cheaper.
- The dedicated rail freight corridors that link to two IMEC ports of Mundra (Gujrat) and the Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (Mumbai) will play into IMEC logic.
- But these rail projects skirt southern India, by and large. Containers in the south typically find their way to the Colombo transshipment container terminal via Chennai, Tuticorin/Thoothukudi and so on.
- The south can potentially leverage IMEC that promises to cut delivery schedules by 40% if it also sees dedicated freight corridors as part of an all-India network. Thus, IMEC aims to reduce transportation costs and time for the movement of goods between India, the Middle East, and Europe, making trade more efficient and competitive.
What is the possible template that can be drawn?
- IMEC will have to undergo a key debottlenecking. Haifa cannot be India’s main gateway to the West since its current container traffic is barely one third of Mundra or JNPT and a tenth of India’s current container exports.
- According to some researchers, IMEC will likely draw U.S., European, and Saudi financing, coupled with Indian financing and implementation capacity, particularly in ports.
- The United States International Development Finance Corporation funding for Adani Ports-owned Colombo deepwater container terminal could be a template for Haifa.
Conclusion:
To overcome the present challenges, sustained commitment and cooperation from the participating nations will be essential. The US, with its robust security apparatus and extensive experience in counter-terrorism, can play a key role in supporting the IMEC.
BEYOND EDITORIAL
What are the potential benefits of IMEC?
The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) has the potential to bring several benefits to the participating countries and the region as a whole. Some of the key benefits include:
- Decreased transportation costs and time: IMEC aims to reduce the time and cost of transporting goods between India, the Middle East, and Europe, benefiting consumers and businesses
- Increased trade and investment: The project is expected to promote trade and investment between the regions, fostering economic growth and development
- Job creation: IMEC is likely to create new and improved jobs in various sectors, including infrastructure development, logistics, and manufacturing
- Energy and clean energy: The corridor will facilitate the transportation of clean energy, such as hydrogen, and support the development and export of clean energy technologies
- Improved infrastructure: IMEC will involve the construction of dedicated rail networks, fiber-optic data lines, and hydrogen pipelines, among other infrastructure projects
- Deepened physical connectivity: The project has the potential to deepen physical connectivity between the participating countries, unlocking commercial opportunities and reshaping global trading routes
- Diversification of the financial economy: IMEC is expected to diversify the region's financial economy, improving security and stabilizing the region's economy
- Geopolitical benefits: The project has the potential to improve relations between the participating countries and contribute to regional stability
IMEC has the potential to bring significant economic, social, and geopolitical benefits to the participating countries and the region as a whole.
Mains PYQs
Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyze India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian Countries (UPSC CSE 2017)
Q. How will I2U2 (India, Israel, UAE and USA) grouping transforms India's position in global politics? (UPSC CSE 2022)


