Relevance: GS III
News Excerpt:
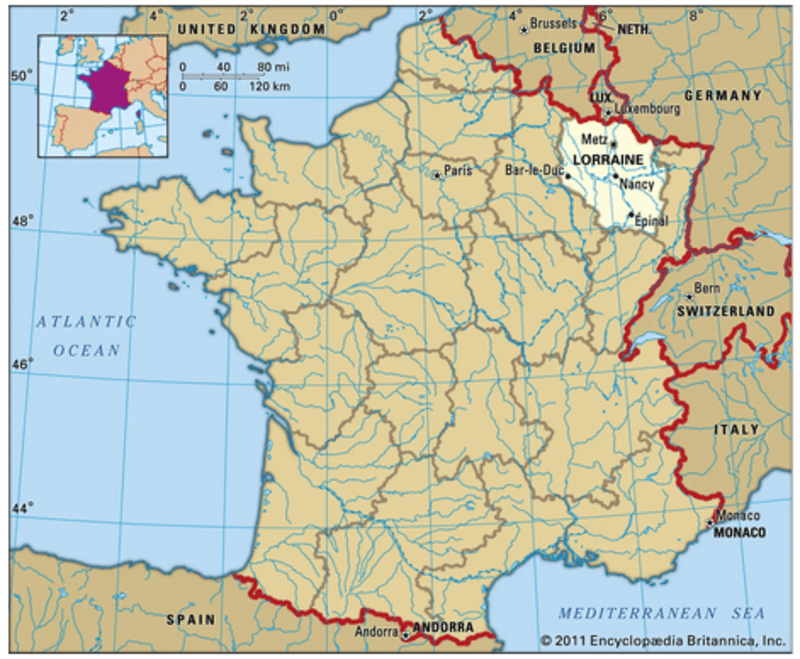
Scientists discovered a large reservoir of naturally occurring "white hydrogen" in northeastern France while assessing methane concentrations in the subsoils of the Lorraine mining basin.
- It is a potentially abundant substance and a great source of clean-burning energy.
What is White Hydrogen?
- Hydrogen, the lightest element on earth with symbol "H" and atomic number 1 is a gas in standard conditions.
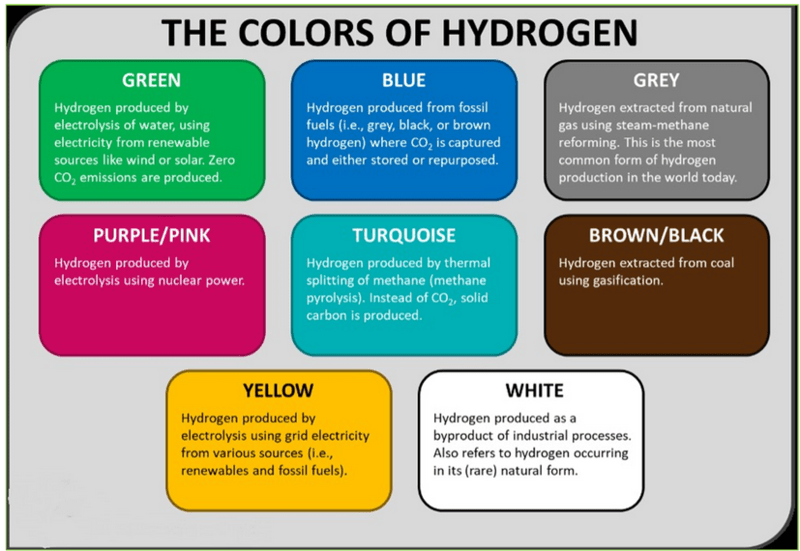
- White hydrogen, also known as natural hydrogen, is a gaseous form of hydrogen that exists naturally within geological formations.
- Unlike its counterparts, such as gray and blue hydrogen derived from fossil fuels, white hydrogen is not a byproduct of industrial processes but is a primary energy source found deep within the Earth's crust.
- The Geological Society of America (GSA) forecasts that the demand for hydrogen will quintuple by 2050, with about 100 megatons of hydrogen currently used annually for industrial processes. GSA calculates that white hydrogen could meet at least half of the global demand for sustainable and clean hydrogen by 2100.
| History of Hydrogen: In 1766, Henry Cavendish was the first to recognize hydrogen gas as a discrete substance, by naming the gas from a metal-acid reaction "inflammable air". In 1783, Antoine Lavoisier gave the element the name hydrogen (from the Greek words- hydro meaning "water" and genes meaning "former"), when he and Laplace reproduced Cavendish's finding that water is produced when hydrogen is burned. |
Why White Hydrogen Matters?
- The significance of white hydrogen lies in its potential to revolutionize the energy landscape by providing a renewable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources.
- White hydrogen is considered highly promising from a climate perspective because it produces only water when burned, making it an attractive clean energy source for various industries such as aviation, shipping, and steel production.
Where White Hydrogen Resides?
- Geologically, white hydrogen can be found in various locations around the world, concealed within the Earth's crust and often discovered accidentally during geological surveys or explorations for fossil fuels.
- Recent discovery was in the Lorraine region of France. It was also found in a few regions of Serbia. While these initial findings hold promise, the accessibility and extraction of white hydrogen from such reserves remain subject to further exploration and technological advancements.
How White Hydrogen Is Extracted and Utilized?
- White hydrogen is extracted by drilling into geological formations and using hydraulic fracturing (fracking).
- The process involves injecting a mixture of water, sand, and chemicals at high pressure to release the hydrogen gas from rocks. In fuel cell vehicles, hydrogen can be converted into electricity, presenting a promising alternative to traditional fuel sources and contributing to the reduction of harmful emissions.
Advantages of White Hydrogen:
- Clean Energy Source: White hydrogen is a clean and environmentally friendly energy source. When burned, it produces only water vapor, resulting in minimal greenhouse gas emissions. This makes it a valuable tool in efforts to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. This makes it a sustainable choice for energy production.
- Decarbonization: One of the most significant benefits of white hydrogen is its potential to decarbonize various industries. It can replace carbon-intensive processes, particularly in sectors like steel, aluminum, and fertilizer production. By utilizing white hydrogen, these industries can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
- Reduced Air Pollution: By replacing fossil fuels in power generation and transportation, white hydrogen helps reduce air pollution. Traditional fossil fuels emit pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, which have adverse effects on air quality and public health. White hydrogen's combustion emits none of these harmful pollutants.
- Energy Security: Utilizing white hydrogen as an energy source can enhance energy security by reducing dependence on fossil fuels and foreign sources of energy. As a domestically available and renewable resource, it can strengthen a nation's energy self-reliance.
- Global Energy Transition: As the world shifts toward cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, white hydrogen can play a pivotal role in the global energy transition. It aligns with international efforts to meet climate goals and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: White hydrogen significantly reduces the carbon footprint in various applications, making it a crucial tool in addressing the global carbon crisis. It contributes to a more sustainable and eco-friendly energy landscape.
Challenges associated with White Hydrogen:
- Extraction Costs: Extracting white hydrogen from underground geological formations can be expensive. The initial investment costs can be a barrier to the development of white hydrogen reserves hence, research and development are needed to refine and optimize these processes.
- Environmental Concerns: The extraction of white hydrogen may raise environmental concerns, particularly regarding the impact on local ecosystems and groundwater. The use of fracking to release the gas from rocks can lead to groundwater contamination, methane emissions, and habitat disruption.
- Safety Precautions: Hydrogen is a highly flammable gas, and its extraction and storage require rigorous safety precautions. Preventing any interaction between hydrogen and atmospheric oxygen is crucial to avoid explosions or fires. Specialized well-protection protocols are essential to manage these risks effectively.
- Distribution and Infrastructure: Unlike other forms of hydrogen, white hydrogen is typically found in remote underground locations. Building the infrastructure for extraction, storage, and transportation to end users can be logistically challenging and costly. The lack of existing pipelines and distribution networks for white hydrogen is a significant hurdle.
- Distance from Demand Centers: Many white hydrogen deposits are located far from the major demand centers, increasing transportation costs and energy losses. Delivering white hydrogen to areas where it is needed, such as industrial facilities or fueling stations, may require substantial investment in distribution networks.
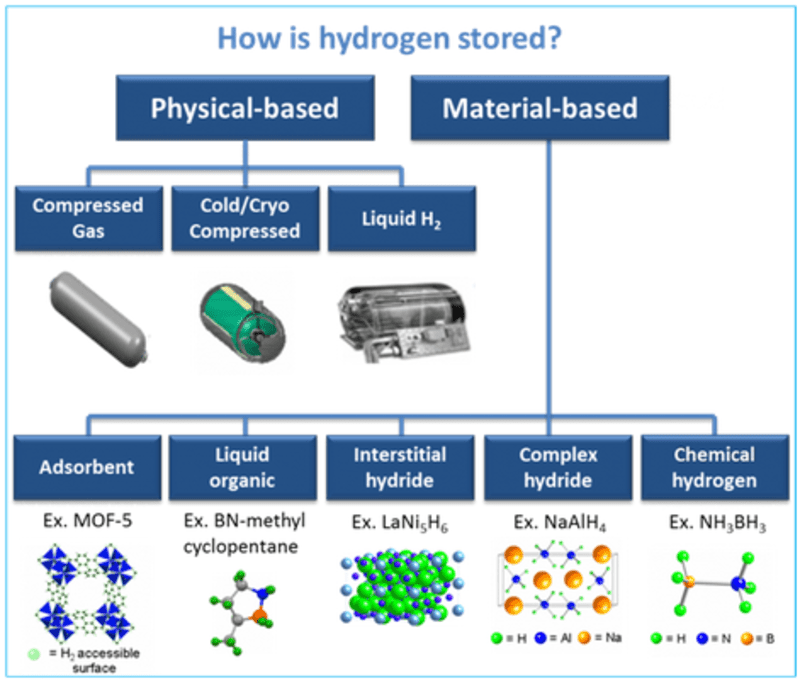
- Energy Intensive Compression and Liquefaction: White hydrogen needs to be stored under high pressure (up to 700 bar) to address volume constraints. Additionally, it must be cooled to extremely low temperatures (around minus 253 degrees Celsius) to transition into a liquid state. These processes are energy-intensive and can result in increased costs.
- Unknown Reserves: While some promising white hydrogen reserves have been discovered, their actual size and quality are often uncertain. Comprehensive exploration and assessment are necessary to determine the reserves' reliability and economic potential.
Way Forward:
- White hydrogen represents a promising avenue for advancing the global shift toward sustainable and renewable energy sources.
- Its natural abundance and clean energy properties position it as a key player in the ongoing efforts to combat climate change and reduce the environmental impact of traditional energy production.
- While challenges related to extraction, storage, and distribution persist, ongoing research and technological advancements offer hope for overcoming these obstacles and realizing the full potential of white hydrogen as a sustainable and eco-friendly energy solution.
PYQs
Q1). 'Clean energy is the order of the day.' Describe briefly India's changing policy towards climate change in various international fora in the context of geopolitics. (2022)
Q2). Write a note on India’s green energy corridor to alleviate the problem of conventional energy. (2013)


