News Excerpt:
For the most recent discovery, scientists used modelling and ecological and metabolic theory to understand how ammonia and inorganic phosphorus in Enceladus' water may favour life on the moon.
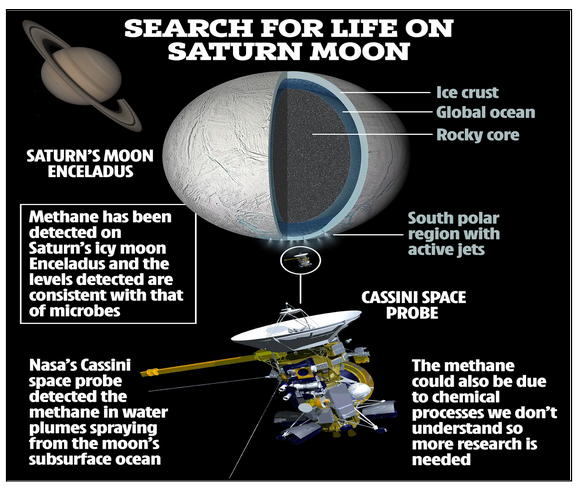
What is Enceladus?
- Enceladus is the sixth-largest moon of Saturn. It is about 500 kilometres in diameter, about a tenth of that of Saturn's largest moon, Titan.
- It is mostly covered by fresh, clean ice, making it one of the most reflective bodies of the Solar System.
Scientists are trying to Discover life-favouring chemicals on Enceladus:
- Cassini discovered geyser-like plumes of water erupting through Enceladus' icy shell during its mission with its Cosmic Dust Analyzer (CDA).
- It showed that the water in the plumes contained a surprising mix of volatiles, including carbon dioxide, water vapour, and carbon monoxide.
- The mission also found trace amounts of molecular nitrogen, simple hydrocarbons, and complex organic chemicals.

New findings:
- A new paper, titled "Observations of Elemental Composition of Enceladus Consistent with Generalized Models of Theoretical Ecosystems", has unveiled new findings.
- The researchers have used ecological and metabolic theory and modelling to understand how ammonia and inorganic phosphorous in Enceladus' ocean could make the moon favourable for life.
- The analysis could be related to the Redfield ratio which is the consistent atomic ratio of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus found in marine phytoplankton and throughout the deep oceans.
- In his study in 1934, he discovered the ratio of carbon to nitrogen to phosphorous (C: N:P) was remarkably consistent across ocean biomass at 106:16:1.
- The study has noted that the analysis of Cassini's data from Enceladus' plumes shows a high level of inorganic phosphate in the ocean.
- These reports of "phosphorus follow on the tails of previous work identifying numerous elemental constituents of terrestrial life (C, N, H, O) from the Enceladus plume.
Hence, Enceladus' ocean has a rich chemistry, and many chemicals reflect life's chemical makeup.


