GS Paper III
News Excerpt:
Electric power transmission is fundamental to economic development and prosperity.
About:
Basics of transmitting electricity:
- Any power supply system has three components:
- Generation: Electricity is generated at power plants and smaller renewable-energy installations.
- Transmission: It is then transmitted via a distributed network of stations, substations, cables, transformers, etc.
- Distribution: Electricity is finally distributed to consumers based on their needs.
- Transmission efficiency: Electricity is transmitted through conductors with higher transmission efficiency at lower current and higher voltage.
- Transformers increase voltage and reduce current before feeding into transmission lines.
- Energy loss: The thickness of the cables affects the energy loss, with thicker cables losing less energy but costing more.
- Cost: The transmission cost decreases with longer distances.
- Electric power transmission is more complex due to multiple phases of electric current, voltage, impedance, frequency, etc.
Two types of electricity:
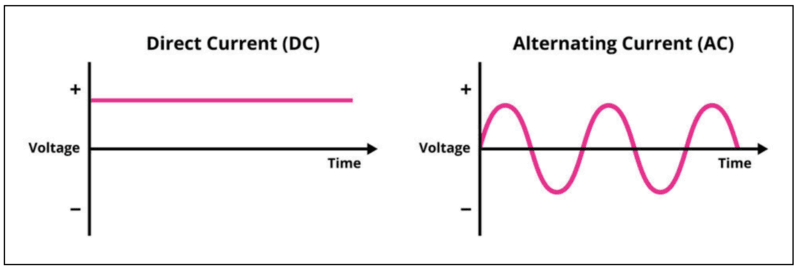
- Direct current (DC):
-
- It is a method in which the voltage is always constant.
- The electricity flows in a certain direction, as compared to the flow of a river.
- It refers to the flow of electricity obtained from batteries, solar cells, etc.
- Alternating current (AC):
- It is a method in which the voltage periodically changes from positive to negative and vice-versa.
- The direction of the current also periodically changes accordingly.
- This is the flow of electricity obtained from a generator or outlet. The electricity produced at power plants and sent to homes is also transmitted as alternating current.
- AC is easier to control than DC, and most appliances are designed to use it.
- It is used for higher transmission efficiency, but the frequency affects the amount of resistance the current faces.
- Engineers model these factors to understand energy loss between generation and consumption.
Process of power transmission:
- Power is transmitted through a three-phase AC circuit, where each wire transmits an AC current in a different phase.
- Transformers step-up the voltage, and the cables are suspended from transmission towers.
- Circuit-breakers break the circuit if there's too much current, and arresters prevent sudden increases in voltage.
- Dampers prevent vibrations in the cables from affecting the towers' stability.
- Switches control the availability of current and move currents between different lines.
- Wires lead to and exit from substations, requiring their support and safety infrastructure.
Operation of grids:
- The national grid integrates power production, transmission, and distribution.
- Grids are designed to adapt to the unique requirements of different power sources which may be located in various areas and consumed in different ways.
- They are also designed to adjust to fluctuations in consumer demand, prevent network failures, regulate voltage and frequency, and enhance power factor.
- A wide-area synchronous grid is formed if all connected generators produce an AC current at the same frequency.
- This results in lower power costs and requires measures to prevent power-supply failures.
- The world’s largest grid covers Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, and Russia; the world’s most powerful is the North Chinese State Grid, with a connected capacity of 1,700 GW.
- India’s national grid is also a wide-area synchronous grid.
- Energy storage facilities and systems that provide power on short notice are also incorporated.
Prelims PYQ
Q. With reference to ‘fuel cells’ in which hydrogen-rich fuel and oxygen are used to generate electricity, consider the following statements :
(UPSC 2015)
1) If pure hydrogen is used as a fuel, the fuel cell emits heat and water as by-products.
2) Fuel cells can be used for powering buildings and not for small devices like laptop computers.
3) Fuel cells produce electricity in the form of Alternating Current (AC).
Which of the statements given above is / are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3


