
CHAPTER:6 Social Infrastructure & Employment
Introduction-
- India will reward itself with demographic dividends in its Amrit Kaal for 25 years. Quality employment opportunities and working conditions are crucial tools to carve this potential into long-term sustainable growth.
- In the Financial Year 2023, various dimensions of the social sector are recouping lost grounds and reenergizing to meet the vision of "sab ka sath, sab ka vikas and sabka Vishwas".
Social sector expenditure-
- Public Sector Spending Maintaining Pace with the Sector's Growing Importance.
- Between FY18 and FY20, the government's overall spending on social services accounted for almost 25% of all expenditures. In FY23, it rose to 26.6 percent (BE).
- From 21% in FY19 to 26% in FY23, health spending as a percentage of overall social services spending has increased.
- Keeping with the objective of the 15th Finance Commission to increase health expenditure to 2.5% of GDP by 2025, Central and State Governments' budgeted expenditure on the health sector reached 2.1 percent of GDP in FY23 (BE) and 2.2 percent in FY22 (RE), against 1.6 percent in FY21.
Improving human development parameters-
- According to the UNDP report, 90 percent of countries have registered a reduction in their Human Development Index (HDI) value in 2020 or 2021, indicating that human development worldwide has stalled for the first time in 32 years.
- The 2021/2022 HDI report placed India at 132 out of 191 countries and territories.
- On the parameter of gender inequality, India's Gender Inequality Index (GII) 9 value is 0.490 in 2021 and is ranked 122. This rating is higher than that of South Asia.
|
UNDP multidimensional poverty Index for India 16.4 percent of the population in India (228.9 million people in 2020) is multidimensional poor, while an additional 18.7 percent is classified as vulnerable to multidimensional poverty (260.9 million people in 2020). India has a 42 percent intensity of deprivation, which is the average deprivation score among those who experience multidimensional poverty. |
Transformation of aspirational district program-
- The Government of India launched the ‘Transformation of Aspirational Districts’ (Identified 117 Aspirational Districts ) initiative in January 2018 with a vision of a New India by 2022.
Achievements of this program-
- In numerous measures related to the theme of "Health and Nutrition," which is tracked by the programme, many aspirational districts have outperformed typical state values. For instance, 73 ADs have outperformed state averages in 10 health indices.
- Across all parameters, districts have all seen significant improvements. In the area of health and nutrition, for instance, 46 districts have witnessed improvements of up to 45%. When examining the results of financial inclusion, it was discovered that aspirational districts outperformed non-aspirational districts.
- According to several aspiring district ADs, fundamental infrastructure measures like the proportion of families with access to electricity and all-weather roads have reached saturation.
- Template of good Governance: - At present, two programs have been conceptualized along the lines of ADP design, one is ‘Mission Utkarsh’ and the other is the ‘Aspirational Blocks Programme’ (ABP).
Labor reforms
- Effective labour laws have been enacted, and technology has been used, such as web-based inspection, to enhance accountability and transparency in enforcement.
|
Code related to labor reforms-
|
- E-shram portal:
- The Ministry of Labour and Employment (MoLE) has developed eShram portal for creating a first-ever National database of unorganized workers, which is verified with Aadhaar.
- For seamless service facilitation, the NCS portal and ASEEM portal are currently connected to the e-Shram portal.
Aadhaar: the many achievements of the unique identity-
- Aadhaar – Usage in DBT: The number is sufficient to transfer any payment to an individual’s bank account through Aadhaar Payment Bridge (APB).
- Aadhaar Enabled Payment Systems (AEPS): This has immensely facilitated providing door-step banking services and helped mitigate the hardships of the people due to the Covid-19 pandemic.
- JAM (Jan-Dhan, Aadhaar, and Mobile) trinity, has helped marginalized groups of society access the formal financial system through the power of DBT.
- One Nation One Ration Card (ONORC) Scheme: Free distribution of food grains under ‘Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana’ (PMGKY) has greatly mitigated the Covid pandemic’s impact.
- PM Kisan Samman Nidhi: Improving Employment Trends.
Improving employment trends-
- Labour markets have recovered beyond pre-COVID levels, in both urban and rural areas with unemployment rates both falling from 5.8% in 2018-19 to 4.2% in 2020-21 and a noticeable rise in rural FLFPR from 19.7% in 2018-19 to 27.7% in 2020-21.
- According to ASI 2019–20 figures, employment in the organized manufacturing sector has also increased over time.
Role of SHGs in women empowerment-
- India has around 1.2 crore SHGs, 88 percent being all-women SHGs. Kudumbashree in Kerala, Jeevika in Bihar, Mahila Arthik Vikas Mahila Mandal in Maharashtra, and most recently Looms of Ladakh are examples of successful organizations.
- Impact of SHGs: Women's economic SHGs have a favorable, statistically significant impact on the economic, social, and political empowerment of women. These favorable effects on empowerment can be attained in a variety of ways.
- Quarterly PLFS for urban areas:- The labor participation rate increased to 47.9 percent in July-September 2022 from 46.9 percent a year ago, while the worker-population ratio strengthened from 42.3 percent to 44.5 percent in the same period.
Formal employment-
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rojgar Yojana (ABRY), launched in October 2020- total registration under the scheme is 75.1 lakh, and total benefits of `8,210 crores have been given to 60.2 lakh beneficiaries through 1.5 lakh establishments till now.
- Demand for work under MGNREGS:- From July to November 2022, it was observed that the number of people requesting employment via MGNREGS was roughly heading towards pre-pandemic levels.
|
National career service projects-
|
- National Career Service Project:- More than 9,100 job fairs have been held as part of the Project, which has registered 2.8 crore job seekers and 6.8 lakh companies. Additionally, 2.5 lakh active vacancies and 1.2 crore total vacancies have been mobilised.
Ensuring a quality education for all-
- The nation's first education policy for the twenty-first century, NEP 2020, was established with the intention of addressing the nation's numerous and pressing developmental needs.
- In order to provide inclusive and equitable quality education at all stages of schooling, Samagra Shiksha was launched in 2018 as an umbrella initiative for the school education sector, stretching from preschool to class XII.
- Gross Enrolment Ratios (GER) in schools and gender parity both improved in the FY22. GER for both boys and girls in classes I to V as a percentage of the population between the ages of 6 and 10 years has increased in FY22.
- School Dropout: In recent years, there has been a steady fall in all levels of school dropout rates. Both boys and girls are experiencing a drop.
- School Infrastructure: The education infrastructure in the form of schools, amenities, and digitalization has been steadily promoted along with a focus on pedagogy.
- Further, the availability of teachers, measured by pupil-teacher ratio, an indicator that is inversely related to improvement in the quality of education, has improved at all levels continuously from FY13 to FY22.
- PM Schools for Rising India:. These schools will have cutting-edge facilities, demonstrate how the NEP is being implemented, and eventually become models for other schools in the area as they take on leadership roles. In accordance with the plan, it is possible to establish more than 14,500 PM SHRI Schools between FY23 and FY27 by enhancing the current institutions run by the federal, state, municipal, or UT governments
- The National Curriculum Framework (NCF) for Foundational Stage:- The new 5+3+3+4 curricular structure known as NCF for Foundational Stage has been introduced, integrating early childhood care and education for all kids between the ages of 3 and 8.
- Pilot project of Balvatika: For pupils in the age ranges of 3+, 4+, and 5+ years, there is a focus on developing cognitive, emotional, and psychomotor abilities as well as early reading and numeracy.
- Toy-based pedagogy: To encourage the inclusion of indigenous toys and their pedagogy in the curricula of school education, early childhood care and education, and teacher preparation, a guidebook for Toy-based pedagogy has been created.
- Screening tools (Mobile App) for specific learning disabilities:A mobile app for disability screening called PRASHAST has been released; it covers 21 impairments, including the benchmark impairments listed in the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act of 2016.
- National Credit Framework (NCrF): By incorporating the National Higher Education Qualification Framework (NHEQF), National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF), and National School Education Qualification Framework, the NCrF is an umbrella framework for skilling, re-skilling, up-skilling, accreditation, and evaluation, seamlessly integrating the credits earned through school education, higher education, and vocational and skill education (NSEQF).
- Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS): Over the course of five years, the STARS Project will be implemented as a CSS in six states: Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Odisha, and Kerala
- Vidyanjali (A School Volunteer Initiative): Through community, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), and private sector involvement, the country's schools are to be strengthened and the quality of education it provides improved.
- Samagra Shiksha Scheme: A CSS of Samagra Shiksha of the Department of School Education and Literacy is an overarching program for the school education sector extending from pre-school to class XII.
HIGHER EDUCATION-
Initiatives for higher education-
- Research & Development Cell (RDC) in Higher Education Institutions (HEI):- The University Grants Commission (UGC) initiated an initiative to create an RDC in HEIs with the goal of fostering high-quality research that significantly advances the objective of an independent India, in line with NEP 2020's guidelines.
- Guidelines for pursuing two academic programs simultaneously: The UGC, in April 2022, issued Guidelines to allow students to pursue two academic programs simultaneously keeping in view the objectives envisaged in NEP 2020.
|
Akhil bharatiya shiksha samagam The Ministry of Education hosted a three-day Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Samagam at Varanasi on July 7-9, 2022, in collaboration with the UGC and Banaras Hindu University. |
Equipping the workforce with employable skills and knowledge in mission mode-
- By creating a framework for technical and vocational education, upgrading existing skills, developing new ones, and encouraging creative thinking for both current and future occupations, skill development aims to close the gap between the demand for and supply of skilled labor.
Skill india mission-
- Under the Mission, the government is putting various skill development programs into place all around the nation through more than 20 Central Ministries/Departments.
Quality and affordable health for all
- As part of the National Health Mission, the Government has made a deliberate effort to interact with all significant sectors and stakeholders in order to promote the objectives of achieving universal health coverage and provide high-quality healthcare services to everyone at affordable prices.
Health expenditure estimates-
- The social security expenditure on health, which includes the social health insurance program, government-financed health insurance scheme, and medical reimbursements made to government employees, has increased from 6 percent in FY14 to 9.6 percent in FY19.
Rural healthcare- strengthening of infrastructure and human resources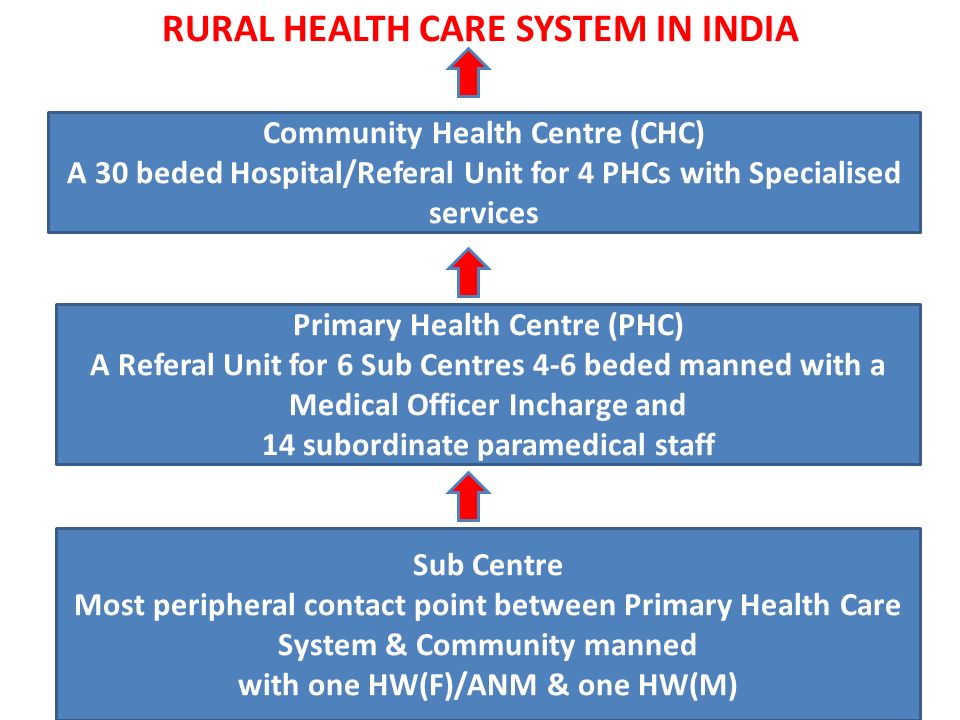
Progress under major government initiatives for health-
- eSanjeevani: It is a cutting-edge, indigenous, affordable, and integrated cloud-based telemedicine system application that enables patient-to-doctor teleconsultation to guarantee a continuum of care and facilitate health services to all residents in the comfort of their homes, at no cost.
- Progress under Ayushman Bharat:- 3 crore beneficiaries are among the 21.9 crore beneficiaries who have had their eligibility for the program verified.
- Deworming: a low-cost high-returns intervention.
National COVID-19 vaccination programme-
- India's national COVID-19 Vaccination program, which is the world's largest vaccination program, began on 16th January 2021, initially with the aim of covering the adult population of the country in the shortest possible time.
Social protection for the rainy day-
- Pradhan Mantri Vaya Vandana Yojana (PMVVY), Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJY), PM Street Vendor’s Atmanirbhar Nidhi Scheme (PM SVANidhi) etc.
- Development of India’s Aspiring Rural Economy :- It presently stands at 65 percent for 2021. Furthermore, agriculture provides a living for 47% of the people. Therefore, it is crucial that the government concentrate on rural development.
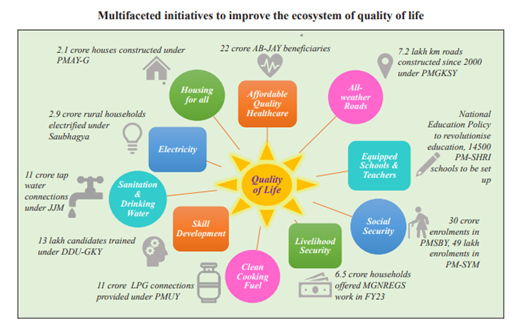
- Enhancing rural income- Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAYNRLM) - The cornerstone of the Mission is its ‘community-driven’ approach which has provided a huge platform in the form of community institutions for women empowerment. At the centre of the programme are rural women
Deen dayal upadhyaya grameen kaushal yojana
- A placement-linked skill development programme called DDU-GKY is offered by the NRLM to rurally disadvantaged children.
- Rural housing: by 2024, all eligible houseless households residing in kutcha and dilapidated dwellings in rural areas will receive around 3 crore pucca houses with essential amenities.
Drinking water and sanitation-
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Since the launch of the Mission, 19.4 crore rural households, 11.0 crore households are getting tap water supply in their homes.
- More than 1.5 lakh villages and Gram Panchayats have also been renamed as "Har Ghar Jal Block," "Har Ghar Jal Panchayat," and "Har Ghar Jal Gaon," respectively.
- Jal Jeevan Mission as an instrument of public health: With the availability of safe and potable drinking water at the doorstep of every rural household, water-borne diseases have drastically reduced from 1.8 crore in 2019 to 59.0 lakh in 2021, as per data from Directorate General of Health Services, M/o Health and Family Welfare "
- Mission Amrit Sarovar- was started on 24 April 2022, National Panchayati Raj Day, with the intention of conserving water for the future. In each district of the nation, 75 water bodies are to be improved and revitalised as part of the mission for this Amrit Varsh, the 75th year of independence..
- JALDOOT App- On September 27, 2022, the JALDOOT app was introduced to measure the water level in a Gram Panchayat using a few carefully chosen open wells twice a year (pre- and post-monsoon).
LPG Connection-
- 1.6 crore connections have been made available through this Ujjwala 2.0 scheme until November 24, 2022..
- Rural connectivity:-
- Pradhanmantri Gram Sadak Yojna: Since its start, a total of 10,383 Long Span Bridges (LSBs) and 1,84,984 roads totaling 8,01,838 km have been approved under all of PMGSY's interventions and verticals.
Electricity-
- On March 31, 2022, the Saubhagya project was successfully finished and shut down.
- Deendayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY)- Since the start of the Saubhagya period in October 2017, 2.9 crore households have been electrified overall through a variety of programs, including DDUGJY and Saubhgaya.
Direct benefit transfer: a game changer
- Over 26.5 lakh crore in total transfers for Central Schemes have been done through the DBT channel since the beginning of the DBT. Due to the removal of 9.4 crore duplicate, false, or nonexistent beneficiaries from databases during this procedure, total savings of more than '2.2 lakh crore have been realized as of 31 March 2021 for Central programs alone.
Enhancing rural convergence for inclusive growth
- Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan- The plan was updated and given the go-ahead in April 2022 for implementation from FY23 to FY26. The focus of the scheme of Revamped RGSA is on reimagining PRIs as vibrant centers of local self-governance with a special focus on the Localisation of SDGs (LSDGs) at the grassroots level.
Conclusion-
- Future advancements will hold the key to achieving more equal economic growth with the idea of "Minimum Government; Maximum Governance." The obvious ones include strengthening community workers' contributions to healthcare, improving learning outcomes through digital and instructional interventions in schools, and supporting SHGs through improved product design and enterprise upscaling.
