News Excerpt:
The rising incidence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) across the globe has become a concern for doctors.
What is Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a term for two conditions (Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative colitis) that are characterised by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
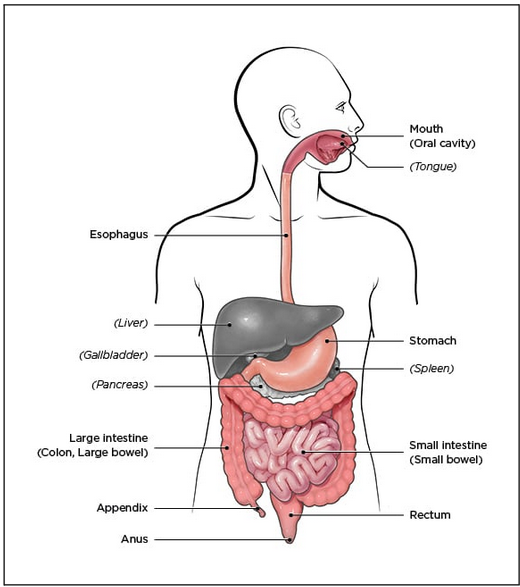
- Ulcerative colitis:
- This condition involves inflammation and sores (ulcers) along the lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum.
- Crohn's disease:
- This type of IBD is characterised by inflammation of the lining of the digestive tract, which often can involve the deeper layers of the digestive tract.
- Crohn's disease most commonly affects the small intestine. However, it can also affect the large intestine and uncommonly, the upper gastrointestinal tract.
- Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease are complex immune-mediated diseases with a dysregulated immune response.
-
- Both ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease usually are characterised by diarrhoea, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, fatigue and weight loss.
- Genetic markers contribute to the disease, but not in isolation. There is a synergy between the external environment and gut bacteria.
- There is an increasing incidence of IBD across the globe, including in North America and Western Europe. While early diagnosis is lacking, diagnosis in itself is challenging, considering that other conditions could mimic IBD.
Early onset of IBD in India:
- In India there is a rise in early onset cases among those under 18 years of age.
- The incidence of IBD has almost doubled in India from 1990 to 2019, with a rise in the death rate as well.
- A study in Tamil Nadu showed that there were more cases of Crohn’s Disease than Ulcerative Colitis.
- Nearly 50% of IBDs were Crohn’s Disease, and 40% were Ulcerative Colitis.
- It is important to catch patients early so treatment is better.
- The symptoms of IBD overlap with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. This does delay diagnosis.
- Individuals with alarming symptoms such as bleeding and severe abdominal pain need a complete evaluation.
- Reasons:
- Changes in lifestyle, a Westernised diet with high fat and high sugar, processed and packaged food cause an insult to the gut epithelium, precipitating inflammation.
Diagnosis:
- There is no single diagnostic test for Ulcerative Colitis or Crohn’s Disease. It is a combination of physical, laboratory, and endoscopy tests.
- Challenges in diagnosing Crohn’s disease:
- Some diseases like intestinal tuberculosis, which is common in India, resemble Crohn’s disease.
- The phenotype of both diseases is very similar, and so is the clinical presentation. As a result it is challenging to diagnose Crohn’s disease.
- As there are other diseases that mimic IBD, there is a need to rule out infection caused by such disease.
Treatment of IBD:
- There is no cure for IBD. It is a lifelong disease.
- Over the last 25 years, biological therapy has emerged that uses monoclonal antibodies directed at inflammatory pathways.
- Biologics have been developed to target different parts of the inflammatory pathways to control the disease, thereby decreasing hospital stays and surgeries.
- In addition, scientists have developed small molecules that can be given orally that have had a significant impact on cases of IBD.
- Faecal microbiota transplantation along with regular medication is also a low cost treatment of IBD.
Diet and environmental factors:
- Environmental factors play a big role in IBD including smoking and antibiotics.
- Some foods such as super-processed foods have the potential to be pro-inflammatory.
- A healthy diet avoiding highly processed food, and consuming wholesome food is recommended.
- The Mediterranean diet is one such diet recommended to IBD patients.
- Diet of curd and buttermilk, rice and millets, fruits, and vegetables is anti-inflammatory and good for patients with IBD.
- One should also avoid red meat and consume fish.
- Although the patients are advised to avoid being restrictive about their diet as they could become malnourished.
