News Excerpt
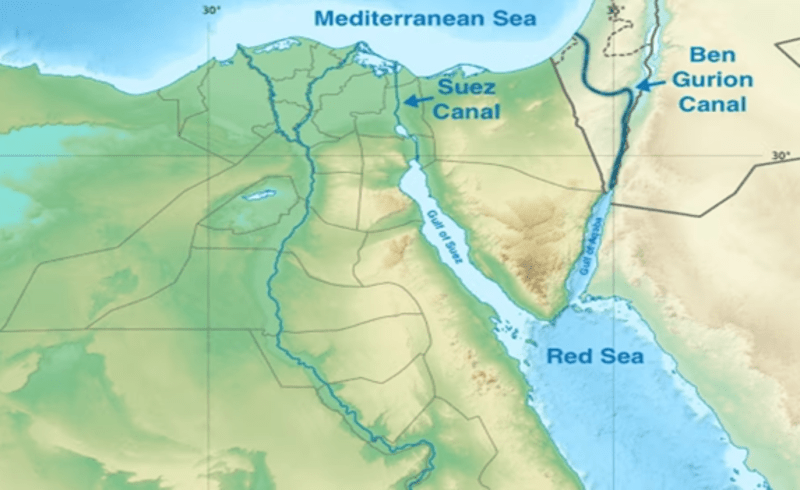
It has been speculated that the world is going to see an alternative to the Egyptian-controlled Suez Canal that starts from the western arm of the Red Sea and passes to the southeastern Mediterranean through the northern Sinai peninsula.
Key Points
- One of the reasons for Israel's desire to eliminate Hamas from the Gaza Strip and completely control the Palestinian enclave is to allow it to better explore an economic opportunity that has been discussed for decades, but for which peace and political stability in the region are necessary prerequisites.
- The plan is to construct a canal through the Israeli-controlled Negev Desert from the tip of the Gulf of Aqaba — the eastern arm of the Red Sea that juts into Israel's southern tip and south-western Jordan — to the Eastern Mediterranean coast.
Gurion Canal Project
- The Ben Gurion Canal Project, which was first envisioned in the 1960s, has the potential to revolutionize global marine dynamics by removing Egypt's stranglehold on the quickest route between Europe and Asia.
- However, any attempt to build the canal would face enormous logistical, political, and funding hurdles, making it appear largely fantasy in the current context.
A look at the Suez Canal’s salience
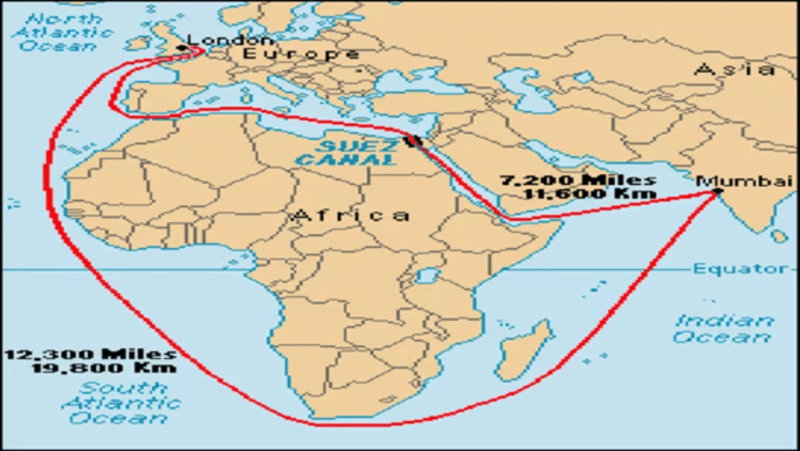
- The Suez Canal, which opened in 1869, changed worldwide maritime trade.
- It meant that ships traveling between Europe and Asia would not have to sail all the way around Africa by connecting the Mediterranean and Red Seas via the Isthmus of Suez.
- The canal reduced the distance between London and Bombay (now Mumbai) by about 41%.
- In the fiscal year 2022–23, nearly 26,000 vessels passed through the Suez Canal, accounting for approximately 13% of global shipping.
Issue with Suez Canal
- First, the Suez Canal, which is 193 kilometres long, 205 meters wide, and 24 meters deep, is the world's largest shipping bottleneck. Despite being extended and deepened over the years, it is always congested, with long lines at each end.
- The massive cargo ship Ever Given got stuck in the canal in March 2021, halting access for more than a week. Every day, the resulting "traffic jam" was predicted to hold up $ 9.6 billion in products.
Suez Crisis:
- Egypt's ownership over the waterway has been a cause of contention for nearly 70 years. After Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser (1918–70) decided to nationalise the canal, war broke out, with the United Kingdom, France, and Israel fighting Egypt to reclaim control.
- The Suez Crisis ended with a military success for the aggressors but an overwhelming political victory for Egypt, which retained control of the canal, which had been closed due to the fighting for more than six months. This was also an important turning point in the Cold War, with Soviet involvement threats critical to halting the allied attack against Egypt.
- The Suez Canal was also at the heart of both the 1967 and 1973 Arab-Israeli wars, and it was closed from 1967 until 1975.
Egypt's economy depends on the canal. It collects all toll income generated, as well as the benefits it provides to the local economy. According to the World Bank, Egypt's Suez Canal Authority saw toll receipts hit a record $ 9.4 billion in the fiscal year 2022-23, accounting for roughly 2% of Egypt's GDP of $ 476.8 billion.
About New Route
- It is uncertain when the first concrete alternative plan was proposed. A declassified 1963 US government memorandum contains verifiable evidence. The letter proposed using nuclear explosives to build the canal through Israel's Negev Desert.
Conclusion:
Such a canal would be a strategically valuable alternative to the present Suez Canal and would probably contribute greatly to the economic development of the surrounding area.
Prelims PYQ
Q. Southeast Asia has captivated the attention of global community over space and time as a geostrategically significant region. Which among the following is the most convincing explanation for this global perspective? (UPSC 2011)
(a) It was the hot theatre during the Second World War
(b) Its location between the Asian powers of China and India
(c) It was the arena of superpower confrontation during the Cold War period
(d) Its location between the Pacific and Indian oceans and its pre-eminent maritime character
Mains PYQ
Q. What were the events that led to the Suez Crisis in 1956? How did it deal a final blow to Britain’s self-image as a world power? (UPSC 2014)
