GS Paper III
News Excerpt:
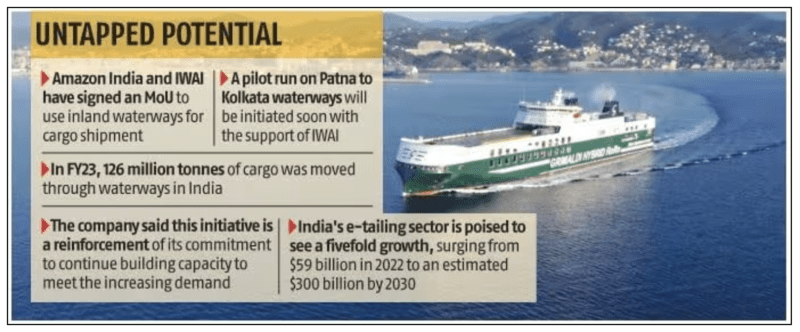
Amazon India and the state-run Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) have signed an agreement that allows the e-commerce firm to use inland waterways to transport customer packages.
More details on news:
- Amazon will be the first e-commerce player in India to use inland water transport.
- Under the MoU, it will work with IWAI to build a network of inland waterways for cargo shipment.
- Using the support of IWAI and its carriers, it will do a pilot run on Patna-Kolkata waterways.
- This partnership seeks to harness the efficiency and sustainability of water transport to optimise logistics, diminish environmental footprints, and promote economic development.
- This initiative will open up new possibilities for all e-commerce companies.
- Inland waterways transport would ensure quicker, sustainable and more reliable delivery of customer packages and widen the reach of sellers.
Growth of India’s e-commerce sector
- There is burgeoning adoption of e-commerce in Tier-II cities and beyond.
- This, combined with a growing base of mass consumers and the expansion of 3PL (third-party logistics) serviceability, catalyses shipment volumes.
- The volumes are projected to rise more sharply than growth in gross merchandise volumes (GMV).
Inland Water Transport (IWT)
- An Inland waterway is a network of rivers, canals, backwaters, and creeks that can be utilised for transportation instead of or in addition to roads and rails.
- According to a World Bank Report, rail and road transport consume 18.5% and 91.6% more fuel than water transport, making it the most environmentally friendly mode of transportation.
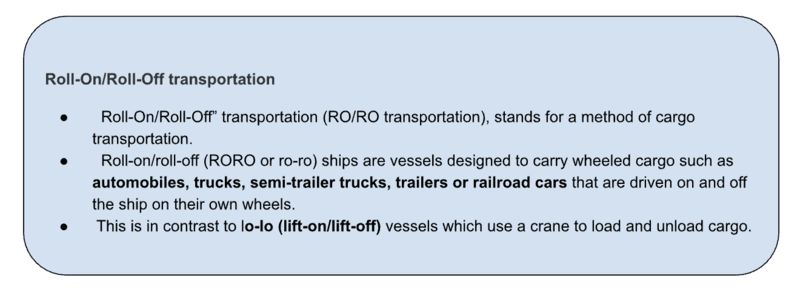
- In addition to cargo movement, the IWT sector also provides a convenient function in related activities such as carriage of vehicles {on Roll-on-Roll-off (Ro-Ro) mode of cross ferry} and tourism.
- Inland water transport has the advantage of cheap transport, especially for heavier loads and long journeys.
Inland water transport in India
- IWT Wing is responsible for developing, managing, and implementing capacity-building and institutional strengthening initiatives in the National Waterways (NWs).
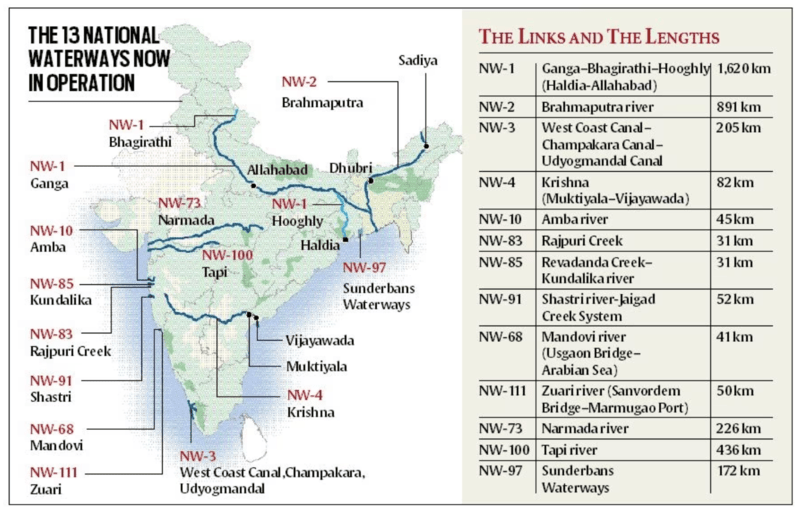
- The Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) is responsible for the development of waterways. The National Waterways Act 2016 has declared 111 inland waterways as ‘National Waterways’ (NWs) to promote shipping and navigation on them.
- The Jal Marg Vikas project is being implemented in NW1 by the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) with the help of the World Bank.
- India has an extensive network of inland waterways with a navigable length of 14,500 km in rivers, canals, backwaters and creeks.
- In India, Inland Water Transport (IWT) has the potential to supplement the over-burdened railways and congested roadways.
Challenges of Inland Waterways
- Underutilised transportation: Freight transportation by waterways is highly underutilised in the country compared to developed countries.
- Limited role: India's hinterland connectivity is mainly based on road and rail, with domestic waterways— coastal shipping and inland waterways—playing a limited role with just 2% of India’s modal mix.
- Seasonal Navigation: During the dry winter & summer seasons, most rivers run dry and do not even have sufficient water for irrigation, so navigation is hindered.
- South India River: Rivers of south India flow through rocky areas. Hence, they are not fit for plying boats because of waterfalls.
- Slow transport: Compared to boats, railways are quicker and more reliable.
- Shallow and sandy delta: Since Indian rivers fall from the shallow and sandy delta, ships cannot sail from seashores to inland parts.
Way forward:
- Integration of transport: To promote a more integrated transportation system, develop intermodal transport hubs that connect inland waterways with existing road and rail networks.
- Developing tourism infrastructure: Promote inland waterway tourism along scenic waterways to attract both domestic and international tourists.
- Encouraging private investment: Promote Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) like the Jal Marg Vikas Project in developing and maintaining inland waterways. For example, e-commerce sites like Amazon and IWA MoU signed.
- Regular dredging: Dredging and channel maintenance is required to maintain adequate depth for navigation.
- Installing modern navigation aids, Such as GPS-based systems and buoys, to enhance the safety and efficiency of navigation along waterways.
